Introduction: When the World Becomes Too Bright
Experiencing sudden or chronic Light Sensitivity (Photophobia) is more than just a minor inconvenience; it is a vital distress signal from your neurological and ocular systems that requires immediate attention.
Photophobia is not a disease in itself; it is a neurological and ocular distress signal. In our 2025 digital landscape—filled with high-intensity LED screens and artificial blue light—our eyes are more vulnerable than ever. This guide will deconstruct the causes of photophobia, identify your specific triggers, and provide a clinical roadmap for natural relief.
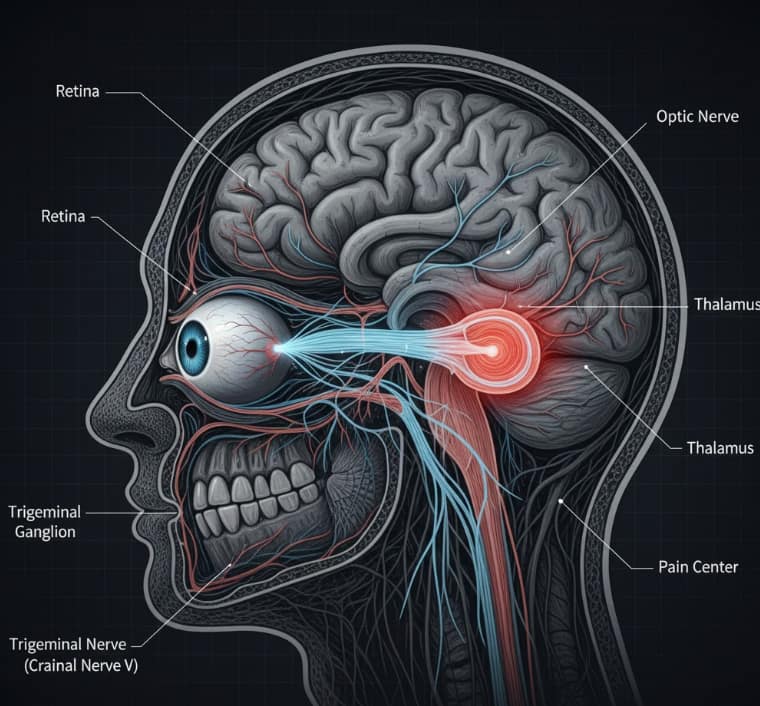
What is Photophobia? The Science of Ocular Pain
At its core, photophobia is an abnormal intolerance to light. While the eye detects light, the Trigeminal Nerve (the largest cranial nerve) processes the pain. When you have photophobia, the communication between your retina and your brain’s pain centers becomes hyper-sensitized.
The Anatomy of a Trigger
- The Retina: Captures light.
- The Intrinsically Photosensitive Retinal Ganglion Cells (ipRGCs): These cells contain Melanopsin, which is highly sensitive to blue light (480nm).
- The Brain: If the system is “primed” by inflammation or a migraine, these cells send a signal that interprets light as literal physical pain.
Quick Diagnostic Table
Identify your urgency level before diving into the causes.
| Symptom | Potential Root Cause | Action Level |
|---|---|---|
| Light + One-sided throbbing | Migraine / Cluster Headache | Moderate (Manageable) |
| Light + Gritty/Burning | Dry Eye Syndrome | Chronic (Biohacking) |
| Light + Sudden Blurred Vision | Acute Glaucoma | 🚨 EMERGENCY |
| Light + Eye Redness + Pain | Uveitis / Iritis | HIGH (Specialist) |
| Light + Recent Trauma | Corneal Abrasion | High (Infection Risk) |
Disclaimer: This table is for informational purposes only. If you experience sudden vision changes or excruciating pain, seek emergency medical care immediately.
The 12 Most Common Causes of Light Sensitivity
1. Migraines and Neurological Triggers
Over 80% of migraine sufferers experience photophobia. This is often due to Central Sensitization, where the brain remains in a state of “high alert,” making even dim light feel unbearable.
2. Chronic Dry Eye Syndrome (DES)
When the tear film is unstable, the corneal surface becomes irregular. This causes light to scatter (diffract) across the eye instead of focusing cleanly, triggering a sharp sensitivity.
3. Digital Eye Strain (Computer Vision Syndrome)
Modern LED screens emit a specific “flicker” and high-energy blue light. Prolonged exposure fatigues the ciliary muscles, leading to Sudden Light Sensitivity at the end of a workday.
4. Corneal Issues
The cornea is the most nerve-dense part of your body. Any scratch (abrasion) or infection (keratitis) will make light feel like a needle.
5. Medication Side Effects
Certain antibiotics (tetracycline), antihistamines, and blood pressure medications can dilate the pupils or sensitize the retina.
🕶️ The Ultimate Photophobia Protection Kit
Don’t just cope; proactively block the specific pain-triggering wavelengths with these clinically-backed tools.

FL-41 Migraine Glasses
The “Gold Standard” tint, scientifically proven to block the 480nm-520nm light range that triggers photophobia and reduces migraine frequency.
Shop on Amazon →
Premium Anti-Glare Screen Filter
Essential for digital nomads and office warriors. Dramatically cuts harsh reflections, blue light, and flicker, easing digital eye strain and photophobia.
Shop on Amazon →Natural Relief & Biohacking Protocols
1. The Magnesium Glycinate Shield
Magnesium regulates the “NMDA receptors” in the brain. When Magnesium is low, these receptors stay open, allowing pain signals (like photophobia) to flood the brain. Dosage: 300-400mg of Magnesium Glycinate daily.
2. FL-41 Tinted Lenses
Unlike regular sunglasses, FL-41 lenses are precision-tinted to filter out the blue-green wavelengths that irritate the trigeminal nerve. Wearing dark sunglasses indoors actually worsens photophobia over time (Dark Adaptation), while FL-41 provides relief without desensitizing your eyes.
3. Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)
B2 is a powerhouse for mitochondrial health in the retina and brain. Studies show that 400mg of B2 can significantly reduce the frequency of light-triggered migraines.
Specific Vitamins for Light Sensitivity
To truly solve the problem, you must nourish the macula.
- Lutein & Zeaxanthin: These are your “internal sunglasses.” They physically deposit in the retina and act as a filter for high-energy light.
- Saffron Extract: Emerging 2025 research shows Saffron improves Contrast Sensitivity, helping the eye distinguish light and dark more comfortably.
📚 Dive Deeper: Explore More Eye Health Insights
Why Your Eyes Feel Heavy & Tired
Uncover the hidden causes behind persistent eye fatigue, even after sleep.
The Best Eye Vitamins & Supplements
A clinical guide to the essential nutrients for optimal vision health.
Dry Eyes in the Morning: Causes & Solutions
Wake up with comfortable, well-hydrated eyes with these proven methods.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are the primary causes of sudden Light Sensitivity Photophobia?
A: Sudden Light Sensitivity Photophobia can be triggered by various factors, ranging from common migraines and dry eye syndrome to more serious conditions like corneal abrasions or inflammation (uveitis). If you notice a drastic change in your light tolerance, it is essential to identify the underlying trigger to prevent further ocular strain.
Q2: Are LED lights worse for people suffering from Light Sensitivity Photophobia?
A: Generally, yes. LED lights often have a high “blue light spike” and an invisible flicker rate that can trigger neurological discomfort much faster than natural sunlight. For those with chronic Light Sensitivity Photophobia, switching to warm-toned lighting or using FL-41 tinted glasses can provide significant relief.
Q3: Why is Light Sensitivity Photophobia sometimes worse in only one eye?
A: When Light Sensitivity Photophobia affects only one eye, it usually points to a localized issue such as a corneal scratch, localized inflammation (iritis), or early-stage glaucoma. Unlike systemic photophobia caused by migraines, one-sided sensitivity requires an immediate professional evaluation to rule out physical injury to the eye.
Q4: Can wearing sunglasses indoors help with Light Sensitivity Photophobia?
A: While it may offer temporary relief, wearing dark sunglasses indoors can actually worsen Light Sensitivity Photophobia over time through a process called “dark adaptation.” By staying in the dark, your retinas become even more sensitive. Instead, experts recommend using light-filtering indoor lenses that block specific painful wavelengths without over-darkening your
Q5: Is Light Sensitivity Photophobia a permanent condition?
A: In many cases, Light Sensitivity Photophobia is a symptom rather than a permanent disease. By treating the root cause—such as managing Binocular Vision Dysfunction (BVD), healing dry eyes, or using neurological filters—most people can significantly increase their light tolerance and return to a normal daily routine.
Conclusion: A Balanced Approach to Light
Living with light sensitivity (photophobia) doesn’t mean you have to live in the shadows. By identifying whether your trigger is neurological (migraine), surface-level (dry eye), or nutritional, you can build a defense strategy. Use FL-41 tints, optimize your magnesium intake, and protect your retina with lutein.
Take Action: If your light sensitivity is sudden, painful, and accompanied by redness, consult an ophthalmologist immediately. For chronic cases, start your biohacking journey today.
A Note from the Founder
"I started CVT because eye health is personal to me. After losing sight in my left eye due to a childhood injury and managing high intraocular pressure for decades, I’ve dedicated my life to finding the best ways to protect the vision we have. Every piece of advice on this site is researched with that same level of care and responsibility. Thank you for being here."



