🟦 INTRODUCTION
Sleep and eye health are far more connected than most people realize. While you sleep, your eyes are not “resting” — they are actively repairing, rehydrating, and restoring delicate tissues damaged throughout the day by screens, artificial light, dryness, and visual strain.
If you wake up with dry eyes, blurry vision, redness, or eye fatigue, the real cause may not be your screen time alone — it may be your sleep quality.
In this complete guide, you’ll learn:
- how sleep repairs the eyes
- why poor sleep worsens dry eye and eye strain
- how melatonin, magnesium, and omega-3 affect vision
- practical routines and supplements that actually work
This article is written for real people — not doctors — and focuses on practical, safe, and proven strategies.
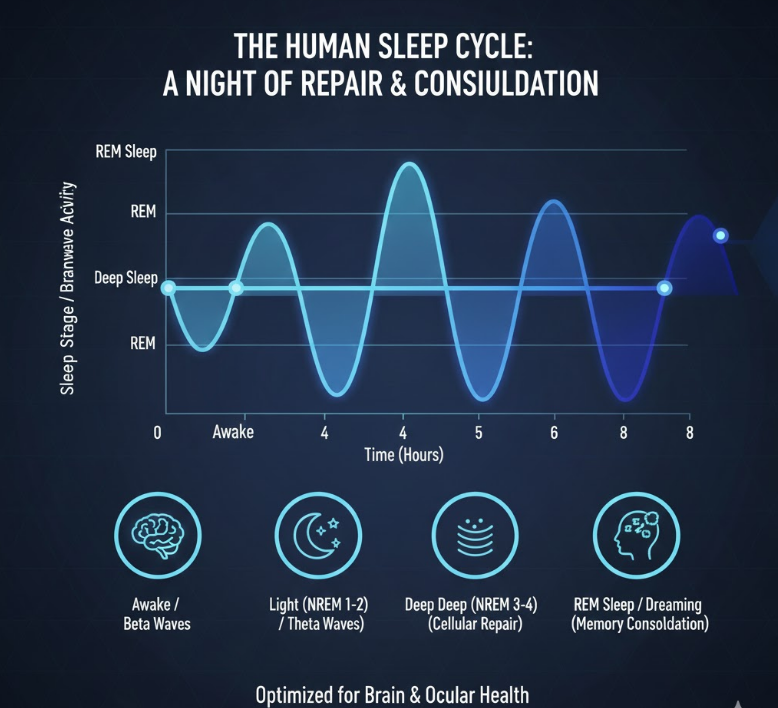
🔹 1. What Happens to Your Eyes While You Sleep
During sleep, your visual system enters repair mode.
Key processes that happen at night:
- regeneration of the tear film
- repair of corneal micro-damage
- reduction of ocular inflammation
- reset of eye-brain signaling
Your eyes rely on deep sleep and REM sleep to recover from daily stress.
🔹 2. Why Poor Sleep Causes Dry Eyes & Blurry Vision
When sleep is disrupted:
- tear production decreases
- inflammation markers increase
- meibomian glands clog more easily
This explains why many people experience:
- dry eyes in the morning
- “filmy” or fluctuating vision
- burning or gritty sensation
People who sleep less than 6 hours per night have up to 2× higher risk of chronic dry eye compared to good sleepers.
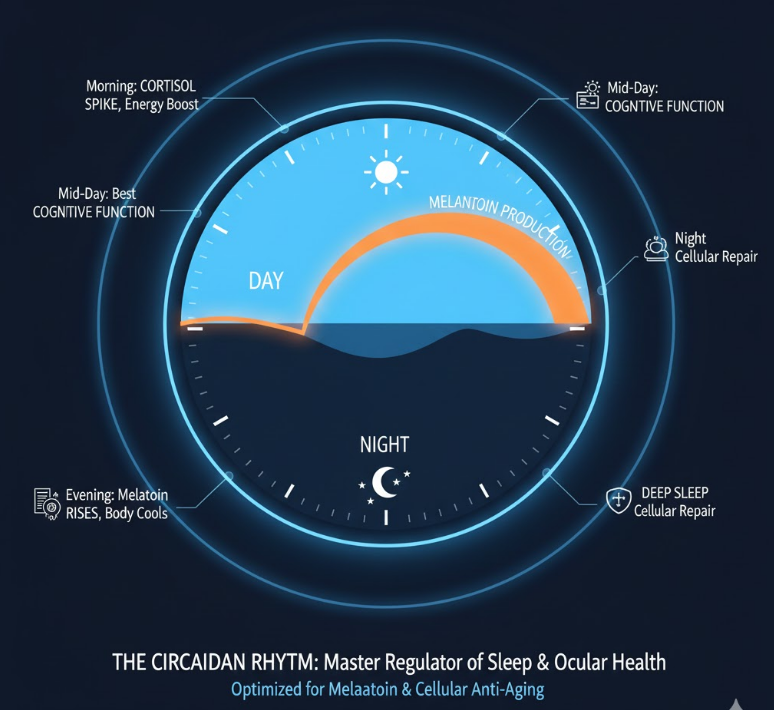
🔹 3. The Role of Melatonin in Eye Health
Melatonin isn’t just a sleep hormone.
Your eyes have melatonin receptors in:
- the retina
- the cornea
- the lacrimal (tear) glands
Proper melatonin signaling:
- protects retinal cells
- reduces oxidative stress
- improves nighttime eye lubrication
Artificial light at night blocks melatonin, delaying eye recovery.
🔹 4. Screens, Blue Light & Nighttime Eye Damage
Using screens late at night causes:
- delayed sleep onset
- reduced REM sleep
- increased eye dryness
Blue light exposure at night keeps your visual system in “day mode”.
Practical fixes:
- stop screens 60 minutes before bed
- use blue-light-blocking glasses after sunset
- enable night mode on all devices
🔹 5. Best Sleep Supplements for Eye Health (What Actually Works)
A) Melatonin (Low Dose Only)
- improves sleep onset
- supports retinal repair
Best dose: 0.3–1 mg
Avoid high doses (3–5 mg) long-term.
B) Magnesium (Glycinate or Threonate)
- relaxes eye muscles
- reduces nighttime eye twitching
- improves sleep depth
C) Omega-3 (EPA + DHA)
- improves tear quality
- reduces eye inflammation
- supports meibomian gland function
✔ High-quality Omega-3 (EPA/DHA)
✔ Supports tear film & eye comfort
✔ Improves nighttime eye recovery
Check price on Amazon →
🔹 6. Nighttime Habits That Damage Your Eyes
Avoid:
- sleeping with contact lenses
- sleeping in dry, air-conditioned rooms
- alcohol before bed
Use:
- humidifier (40–50%)
- preservative-free night eye gel if needed
🔹 7. Sleep Disorders That Affect Vision
Conditions linked to eye problems:
- sleep apnea
- chronic insomnia
- night shift work
Sleep apnea is strongly associated with:
- glaucoma
- floppy eyelid syndrome
- optic nerve damage
🟦 DID YOU KNOW
Did You Know?
Sleep apnea increases glaucoma risk independently of eye pressure, likely due to repeated oxygen deprivation.
🔹 8. Morning Eye Problems Explained
Waking up with:
- dry eyes
- redness
- blurry vision
often means:
- incomplete eyelid closure
- poor tear quality
- mouth breathing at night
Solutions:
- sleep mask
- eyelid hygiene
- omega-3 supplementation
🔹 9. Eye-Friendly Sleep Routine (Simple & Effective)
60 minutes before bed:
- dim lights
- stop screens
- take magnesium
30 minutes before bed:
- melatonin (if needed)
- eye hydration drops
Bedroom setup:
- cool (18–20°C)
- dark
- humidified
🔹 10. When to See an Eye Doctor
Seek evaluation if you have:
- worsening morning blurry vision
- eye pain after poor sleep
- halos or light sensitivity
🔹 FAQ SECTION (Featured Snippet Optimized)
Q1: Can poor sleep permanently damage eyesight?
Poor sleep alone rarely causes permanent damage, but chronic sleep deprivation can worsen existing eye conditions.
Q2: Does melatonin help dry eyes?
Indirectly yes — by improving sleep quality and reducing inflammation.
Q3: Are blue light glasses worth it at night?
Yes, especially after sunset and before sleep.
Q4: Why are my eyes dry only in the morning?
Often due to tear evaporation, mouth breathing, or incomplete eyelid closure.
Q5: Can better sleep improve blurry vision?
Yes — many people notice clearer vision after improving sleep quality.
🔹 CONCLUSION
Sleep and eye health are inseparable. If you want clearer vision, healthier eyes, and less dryness, improving your sleep may be the most overlooked but powerful solution.
Small changes — better sleep hygiene, proper supplements, and light control — can make a visible difference in how your eyes feel every day.
Your eyes don’t just need rest — they need quality sleep.